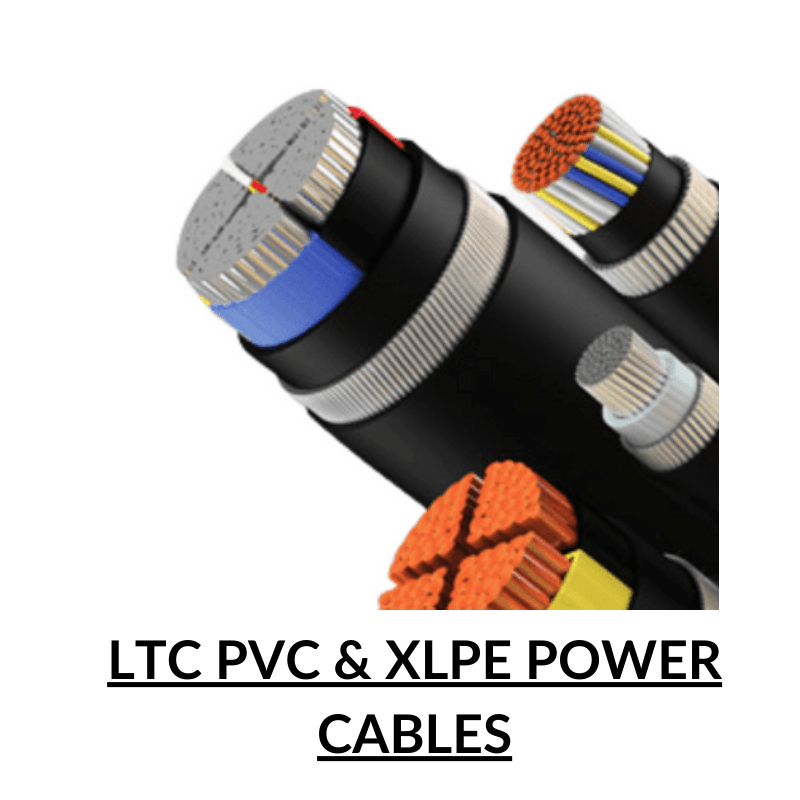
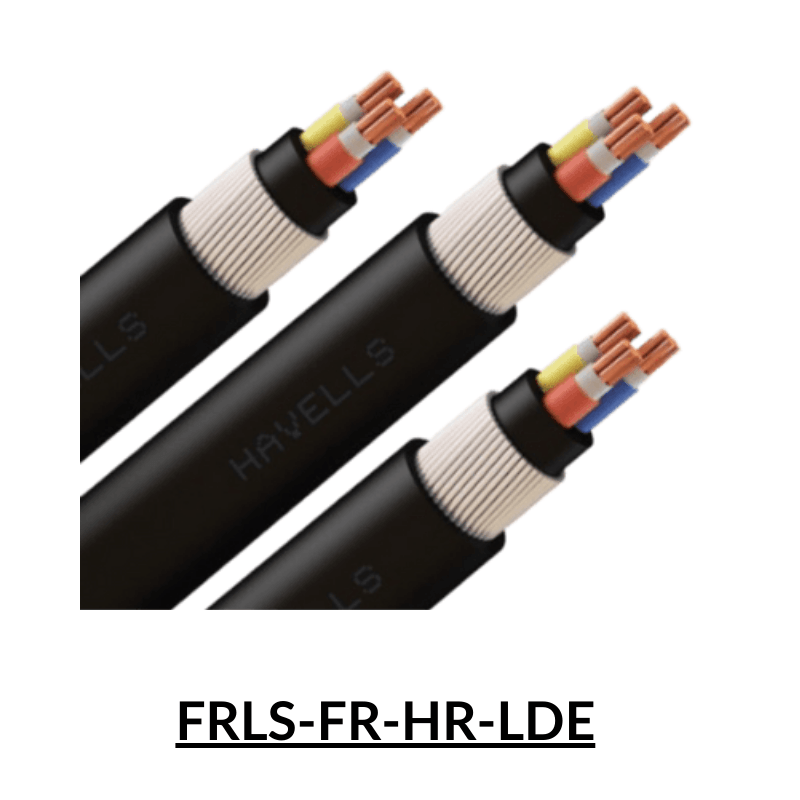
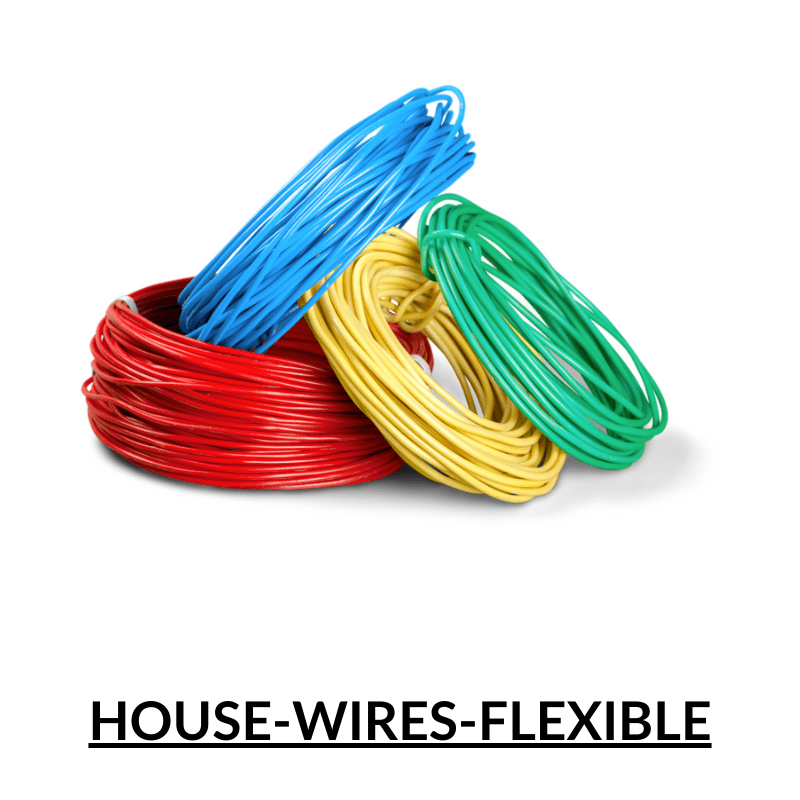
Copper Wire
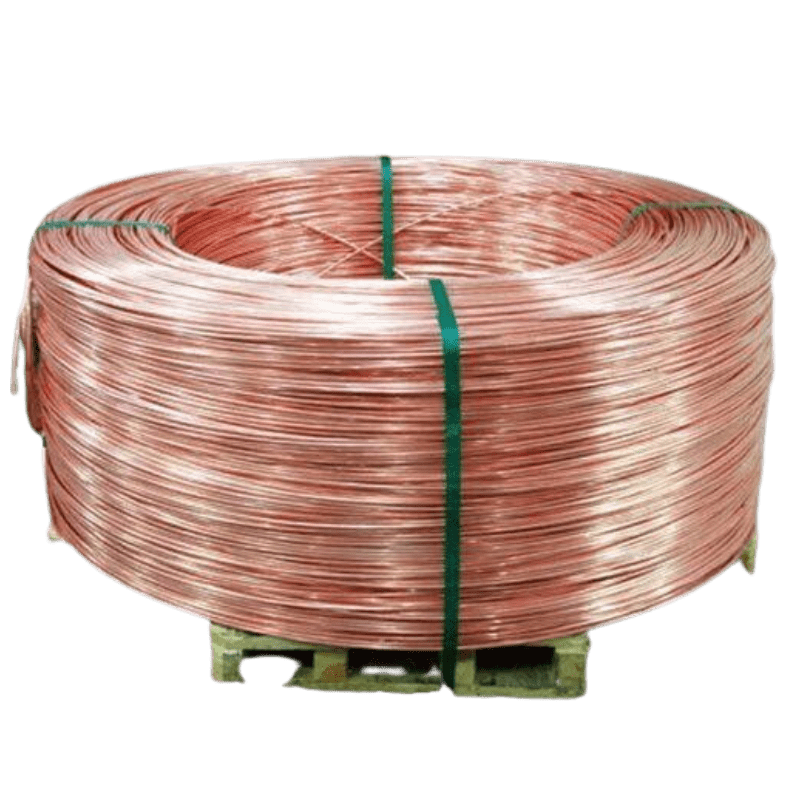
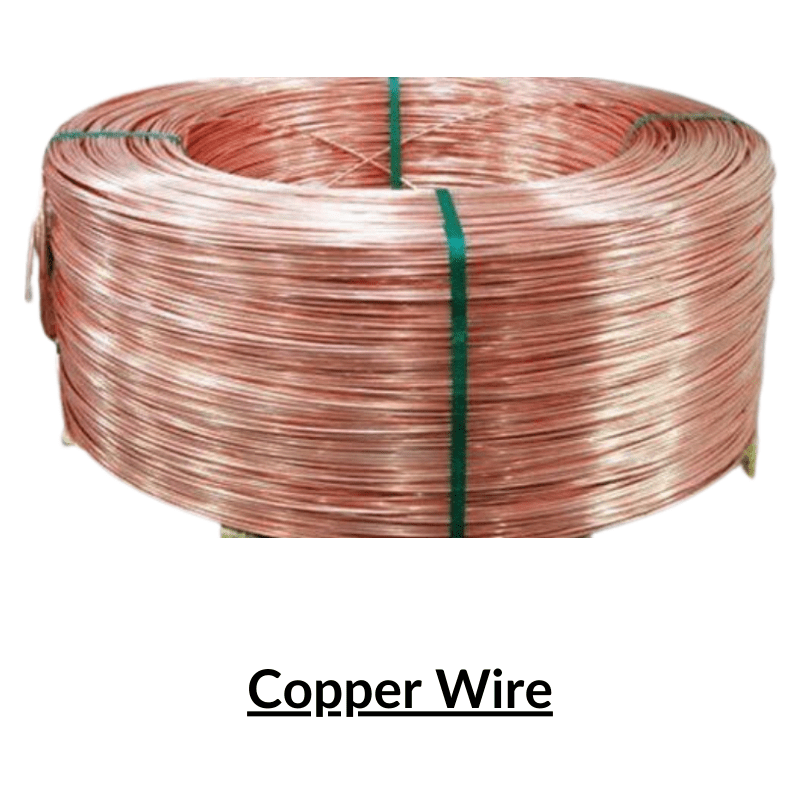
Copper wire is a type of electrical conductor made from copper, which is a highly conductive metal. It is commonly used in electrical wiring and in the manufacturing of electrical components such as motors, transformers, and generators. Copper wire is preferred over other materials for electrical wiring because of its high conductivity, durability, and resistance to corrosion.
Copper wire comes in various sizes, called gauges, which are determined by the diameter of the wire. The larger the diameter of the wire, the lower the gauge number. Copper wire can be solid or stranded, meaning it consists of multiple smaller wires twisted together. Stranded wire is more flexible and easier to work with, while solid wire is more rigid and typically used for applications where stiffness is required.



- High electrical conductivity: Copper is an excellent conductor of electricity, which makes it a popular choice for use in electrical wiring and electrical components.
- Ductility and flexibility: Copper wire is very ductile, meaning it can be easily shaped and formed into different configurations. It is also flexible, which makes it ideal for use in applications where the wire needs to bend or move.
- Resistance to corrosion: Copper wire is highly resistant to corrosion, which means it can withstand exposure to moisture and other environmental factors without deteriorating or breaking down.
- High melting point: Copper has a high melting point, which means it can withstand high temperatures without melting or deforming.
- Durability: Copper wire is very durable and can last for many years without deteriorating or breaking down. This makes it a reliable choice for use in electrical applications.
- Good thermal conductivity: Copper also has good thermal conductivity, which means it can transfer heat efficiently. This property makes it useful in applications where heat needs to be dissipated, such as in electronic components and heat exchangers.
- Electrical wiring: Copper wire is widely used in electrical wiring because of its excellent conductivity, flexibility, and durability.
- Electrical components: Copper wire is used in the manufacture of various electrical components such as motors, transformers, generators, and solenoids.
- Telecommunications: Copper wire is used in telecommunications applications, such as in telephone and internet wiring, due to its excellent conductivity and signal transmission properties.
- Electronics: Copper wire is used in the manufacture of electronic components, such as printed circuit boards, as it provides good electrical conductivity and thermal dissipation.
- Automotive: Copper wire is used in automotive applications, such as in the wiring harnesses and battery cables, due to its high conductivity, durability, and resistance to corrosion.
The high electrical conductivity of copper is due to its atomic structure. Copper atoms have a relatively low number of valence electrons, which allows them to easily share electrons with neighboring atoms. This results in the formation of a network of loosely held electrons, known as a “sea of electrons,” which can easily move through the material in response to an applied electric field. This property of copper, combined with its ductility and flexibility, makes it an ideal material for use in electrical wires and cables.
The insulation on copper wire is usually made of a non-conductive material, such as PVC (polyvinyl chloride) or nylon. The insulation also serves to protect the wire from environmental factors such as moisture, heat, and chemicals.
Explore Our Copper Products
Explore Our Wire & Cables
Copper Wire
Copper wire is a type of electrical conductor made from copper, which is a highly conductive metal. It is commonly used in electrical wiring and in the manufacturing of electrical components such as motors, transformers, and generators. Copper wire is preferred over other materials for electrical wiring because of its high conductivity, durability, and resistance to corrosion.
Copper wire comes in various sizes, called gauges, which are determined by the diameter of the wire. The larger the diameter of the wire, the lower the gauge number. Copper wire can be solid or stranded, meaning it consists of multiple smaller wires twisted together. Stranded wire is more flexible and easier to work with, while solid wire is more rigid and typically used for applications where stiffness is required.
Features
- High electrical conductivity: Copper is an excellent conductor of electricity, which makes it a popular choice for use in electrical wiring and electrical components.
- Ductility and flexibility: Copper wire is very ductile, meaning it can be easily shaped and formed into different configurations. It is also flexible, which makes it ideal for use in applications where the wire needs to bend or move.
- Resistance to corrosion: Copper wire is highly resistant to corrosion, which means it can withstand exposure to moisture and other environmental factors without deteriorating or breaking down.
- High melting point: Copper has a high melting point, which means it can withstand high temperatures without melting or deforming.
- Durability: Copper wire is very durable and can last for many years without deteriorating or breaking down. This makes it a reliable choice for use in electrical applications.
- Good thermal conductivity: Copper also has good thermal conductivity, which means it can transfer heat efficiently. This property makes it useful in applications where heat needs to be dissipated, such as in electronic components and heat exchangers.
Applications
- Electrical wiring: Copper wire is widely used in electrical wiring because of its excellent conductivity, flexibility, and durability.
- Electrical components: Copper wire is used in the manufacture of various electrical components such as motors, transformers, generators, and solenoids.
- Telecommunications: Copper wire is used in telecommunications applications, such as in telephone and internet wiring, due to its excellent conductivity and signal transmission properties.
- Electronics: Copper wire is used in the manufacture of electronic components, such as printed circuit boards, as it provides good electrical conductivity and thermal dissipation.
- Automotive: Copper wire is used in automotive applications, such as in the wiring harnesses and battery cables, due to its high conductivity, durability, and resistance to corrosion.