Lan-cat-5-6e-cables
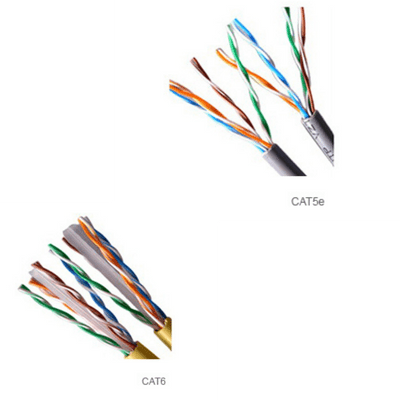
LAN Cat 5 and 6e cables are types of Ethernet cables used for networking. They are designed to transmit data between devices, such as computers, routers, switches, and other network-enabled devices.
Cat 5 cables are capable of transmitting data at speeds of up to 100Mbps (megabits per second) and have a maximum cable length of 100 meters. They are typically used for home networking and small office environments.
Cat 6e cables, on the other hand, are designed to transmit data at speeds of up to 10Gbps (gigabits per second) and have a maximum cable length of 55 meters. They are typically used for larger enterprise networks that require higher bandwidth and faster data transfer speeds.



- Speed: Both CAT5 and CAT6e cables can support high-speed data transfer rates. CAT5 cables can handle speeds up to 100 Mbps, while CAT6e cables can support speeds up to 10 Gbps.
- Bandwidth: CAT5 cables have a bandwidth of up to 100 MHz, while CAT6e cables have a bandwidth of up to 250 MHz. This means that CAT6e cables can transmit more data at higher speeds than CAT5 cables.
- Distance: The maximum distance for CAT5 cables is around 100 meters, while CAT6e cables can transmit data up to 100 meters or more. However, the distance that can be covered depends on various factors such as cable quality, network equipment, and interference.
- Wiring: CAT5 cables have four twisted pairs of copper wires, while CAT6e cables have four twisted pairs of copper wires with additional insulation. The extra insulation reduces crosstalk and interference between the wires.
- Compatibility: Both CAT5 and CAT6e cables are backward compatible, meaning that they can be used with older networking equipment. However, using a higher-grade cable with older equipment will not necessarily improve performance.
- Cost: CAT6e cables are generally more expensive than CAT5 cables due to their higher bandwidth and additional insulation. However, the cost difference may not be significant depending on the length and quality of the cable.
- Cat-5 and Cat-6e cables are types of Ethernet cables commonly used in computer networking. They are designed to transmit data over local area networks (LANs) and are typically used to connect devices like computers, routers, switches, and servers.
- Cat-5 and Cat-6e cables both have four pairs of twisted copper wires that are used to transmit data. The main difference between the two cables is the quality and performance of the copper wire used.
- Cat-5 cables typically use 24-gauge copper wire with a maximum length of 100 meters. The four pairs of wires are color-coded and twisted together to reduce crosstalk and electromagnetic interference (EMI). The wires are also covered with insulation to prevent short circuits and signal loss.
Cat-5 and Cat-6e cables have insulation around each of the four pairs of twisted copper wires to protect against signal loss and cross-talk. The insulation is typically made of a thermoplastic material, such as PVC (polyvinyl chloride), or a thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) material.
Explore Our Copper Products
Explore Our Wire & Cables
Lan-cat-5-6e-cables
LAN Cat 5 and 6e cables are types of Ethernet cables used for networking. They are designed to transmit data between devices, such as computers, routers, switches, and other network-enabled devices.
Cat 5 cables are capable of transmitting data at speeds of up to 100Mbps (megabits per second) and have a maximum cable length of 100 meters. They are typically used for home networking and small office environments.
Cat 6e cables, on the other hand, are designed to transmit data at speeds of up to 10Gbps (gigabits per second) and have a maximum cable length of 55 meters. They are typically used for larger enterprise networks that require higher bandwidth and faster data transfer speeds.
Features
- Speed: Both CAT5 and CAT6e cables can support high-speed data transfer rates. CAT5 cables can handle speeds up to 100 Mbps, while CAT6e cables can support speeds up to 10 Gbps.
- Bandwidth: CAT5 cables have a bandwidth of up to 100 MHz, while CAT6e cables have a bandwidth of up to 250 MHz. This means that CAT6e cables can transmit more data at higher speeds than CAT5 cables.
- Distance: The maximum distance for CAT5 cables is around 100 meters, while CAT6e cables can transmit data up to 100 meters or more. However, the distance that can be covered depends on various factors such as cable quality, network equipment, and interference.
- Wiring: CAT5 cables have four twisted pairs of copper wires, while CAT6e cables have four twisted pairs of copper wires with additional insulation. The extra insulation reduces crosstalk and interference between the wires.
- Compatibility: Both CAT5 and CAT6e cables are backward compatible, meaning that they can be used with older networking equipment. However, using a higher-grade cable with older equipment will not necessarily improve performance.
- Cost: CAT6e cables are generally more expensive than CAT5 cables due to their higher bandwidth and additional insulation. However, the cost difference may not be significant depending on the length and quality of the cable.
Applications
- Cat-5 and Cat-6e cables are types of Ethernet cables commonly used in computer networking. They are designed to transmit data over local area networks (LANs) and are typically used to connect devices like computers, routers, switches, and servers.
Conductors
- Cat-5 and Cat-6e cables both have four pairs of twisted copper wires that are used to transmit data. The main difference between the two cables is the quality and performance of the copper wire used.
- Cat-5 cables typically use 24-gauge copper wire with a maximum length of 100 meters. The four pairs of wires are color-coded and twisted together to reduce crosstalk and electromagnetic interference (EMI). The wires are also covered with insulation to prevent short circuits and signal loss.